How to Hold a Guitar Pick Correctly sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Mastering the grip of a guitar pick is essential for every guitarist, as it not only impacts sound quality but also enhances overall playing technique. With a variety of picks available in different shapes, sizes, and materials, understanding their significance can elevate one’s musical expression.
From the anatomy of the pick to the nuances of grip techniques, this guide aims to provide comprehensive insights that cater to beginners and seasoned players alike. By exploring the relationship between pick selection and playing style, readers will gain a deeper appreciation for this fundamental aspect of guitar playing, ensuring they are well-equipped to enhance their skills and performance.
Introduction to Guitar Picks
Guitar picks, often referred to as plectrums, play a crucial role in shaping the sound and style of guitar playing. They serve as a bridge between the musician’s technique and the instrument, enabling a range of dynamics, tones, and articulations that are essential for expressive playing. Whether strumming chords or executing intricate picking patterns, the correct use of a guitar pick can significantly enhance performance and technique.The variety of guitar picks available allows players to choose one that suits their style, comfort, and desired sound.
Guitar picks come in different shapes, sizes, and thicknesses, each designed to cater to specific playing techniques and musical genres. There are standard picks for general use, jazz picks for precision, and thumb picks for fingerstyle playing. Understanding the options available can empower musicians to select the ideal pick for their expression.
Types of Guitar Picks
There are several types of guitar picks, each designed for particular styles of playing and preferences. The most common types include:
- Standard Picks: Generally triangular in shape, these picks are versatile and commonly used across various music genres.
- Jazz Picks: Characterized by their smaller size and pointed tip, jazz picks offer greater precision and are favored by players who require agility.
- Thumb Picks: Designed to fit comfortably on the thumb, these picks are ideal for fingerstyle guitarists, allowing for a blend of plucking and strumming.
- Finger Picks: Typically worn on the fingers, they enhance fingerstyle playing by providing additional volume and projection.
Understanding the distinct advantages of each type allows guitarists to choose a pick that complements their playing style and enhances their musical expression.
Common Materials Used in Guitar Picks
The material composition of guitar picks significantly influences their performance characteristics, including durability, flexibility, and tonal quality. Common materials include:
- Plastic: The most widely used material for guitar picks, plastic offers a balance between flexibility and control. Variations like nylon and celluloid provide different tonal qualities and feel.
- Wood: Wood picks are known for their warm tone and natural feel. They can vary in density and hardness, affecting the overall sound produced.
- Metal: Metal picks provide a bright, crisp tone with increased durability. They are less common but favored by some players for their unique sound.
- Stone: Stone picks offer a distinct tone and a unique aesthetic appeal. They are heavier and can produce a different attack on the strings.
The choice of material not only affects the pick’s durability but also impacts the player’s technique and the guitar’s sound, making it an important factor in selecting the right pick for individual needs.
Anatomy of a Guitar Pick

Understanding the anatomy of a guitar pick is essential for musicians looking to enhance their playing technique and sound quality. Each component of a pick serves a specific purpose, influencing how it interacts with the strings and the overall performance. This section will delve into the various parts of a guitar pick, the differences between thick and thin picks, and how the shape and size can affect a player’s style and technique.
Components of a Guitar Pick
A guitar pick consists of several key components that contribute to its functionality. These include the tip, the body, and the grip area.
- Tip: The tip of the pick is the part that strikes the strings. A sharper tip provides greater precision and clarity, while a rounded tip offers a warmer tone.
- Body: The body of the pick varies in thickness and material, affecting the overall sound produced. Thicker picks tend to produce a louder, more powerful sound, while thinner picks yield softer tones.
- Grip Area: Some picks feature a textured grip area to enhance comfort and prevent slipping during play. This is particularly beneficial during fast-paced rhythms or intricate solos.
Differences Between Thick and Thin Picks
The distinction between thick and thin guitar picks is crucial for a guitarist’s performance. Each type offers unique benefits that cater to different playing styles.
- Thick Picks: Typically ranging from 0.80 mm to 2.0 mm in thickness, thick picks provide greater control and precision. They are often favored by players who prefer strumming power chords or intricate fingerstyle techniques.
- Thin Picks: Thin picks, usually measuring less than 0.80 mm, produce a softer tone and are ideal for rhythm playing. They allow for more flexibility and are often used in genres requiring fast strumming or delicate fingerpicking.
Influence of Shape and Size on Playing Style
The shape and size of a guitar pick can greatly influence a player’s technique and comfort level. Different shapes cater to various styles of music and personal preferences.
- Standard Shape: The most common shape is the standard triangular design, which provides a balance of comfort and versatility for most playing styles.
- Jazz Picks: Jazz picks are often smaller and have a pointed tip, enabling precise attack and speed, suitable for jazz and other complex styles.
- Large Picks: Some players prefer larger picks for added control, particularly when engaging in heavy strumming or aggressive playing.
“The right pick can enhance your playing experience, offering both comfort and sound quality tailored to your individual style.”
Correct Grip Techniques

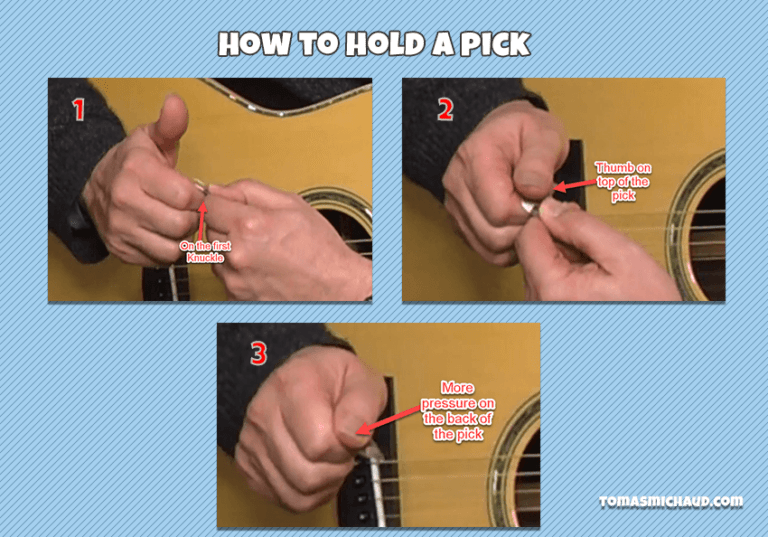
Achieving optimal control while playing guitar is largely dependent on how you grip the pick. The correct grip can enhance precision, comfort, and overall performance, allowing musicians to express their creativity more effectively. This section Artikels the proper techniques for holding a guitar pick.To grip the pick correctly, it is essential to understand how to position your fingers for maximum stability and control.
A well-structured grip ensures that the pick does not slip during play, enhancing your ability to execute various techniques such as strumming and picking. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to properly position your fingers around the pick.
Finger Positioning Around the Pick
Proper finger positioning is crucial for maintaining a steady grip. Follow these steps to ensure your fingers are placed correctly:
1. Hold the Pick with Your Thumb and Index Finger
Position the pick so that it rests between the tip of your index finger and the flat part of your thumb. This creates a stable base for control.
2. Create a Small Angle Between Fingers
Allow your index finger to extend slightly outward, forming a small angle with your thumb. This angle should be around 30 degrees, providing balance without excessive tension.
3. Stabilize with the Middle Finger
Optionally, place the tip of your middle finger against the back of the pick for additional support. This helps to prevent the pick from slipping.
4. Relax Your Grip
Avoid gripping the pick too tightly; a relaxed hold allows for greater flexibility and smoother movement.
5. Test the Grip
Strum or pick a few strings to ensure that the grip feels comfortable and secure without any unnecessary tension. Adjust as needed for your comfort.Common mistakes can hinder the player’s ability to perform effectively. Recognizing and avoiding these pitfalls is essential for developing a proper grip.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Identifying and avoiding common grip mistakes can significantly enhance your playing experience. Here are key points to consider:
Gripping Too Tightly
A tight grip can lead to hand fatigue and reduce sensitivity. Aim for a relaxed hold.
Incorrect Finger Placement
Failing to position the index finger and thumb correctly can result in lack of control. Ensure proper alignment.
Using Excessive Pick Length
A pick that is too long can be difficult to control. Choose a pick size that allows for ease of movement.
Overly Rigid Fingers
Keeping fingers too stiff can limit dexterity. Maintain a natural curve in your fingers for flexibility.
Holding the Pick Too Far Back
Positioning the pick too far back limits the striking area. Hold it closer to the tip for better sound projection and precision.
“Mastering the grip of your guitar pick is foundational to enhancing your performance capabilities.”
Different Playing Styles and Their Pick Use
Understanding the various playing styles in guitar performance is crucial for both aspiring guitarists and seasoned players. Each style requires distinct techniques and grips, influencing not only the sound produced but also the overall comfort and efficiency in playing. The way a guitarist holds their pick can significantly impact their performance, making it essential to adapt grip methods according to specific playing styles.
Strumming Techniques
Strumming is characterized by a sweeping motion across multiple strings, often employed in rhythm playing across various genres. The grip used for strumming tends to be looser compared to that used for picking. A relaxed hold allows for better fluidity and control while providing the rhythmic pulse necessary in styles such as folk, pop, and rock.
- Grip Style: Many strummers utilize a more relaxed grip, typically using the thumb and index finger to hold the pick firmly yet lightly. This approach allows for a natural motion that can adapt to varying dynamics.
- Pick Thickness: Thinner picks (around 0.45mm – 0.73mm) are often favored for strumming, as they produce a softer attack and allow for greater flexibility across the strings.
Picking Techniques
Picking involves targeting individual strings with precision, emphasizing melody and intricate solos. This technique requires a tighter grip to maintain accuracy and control, especially in genres like classical, jazz, and metal.
- Grip Style: The grip for picking is typically firmer, with the pick held closer to the tip of the fingers, allowing for precise movements and quick transitions between strings.
- Pick Thickness: Heavier picks (around 0.73mm and above) are generally preferred for picking, as they offer greater control and a sharper attack, essential for fast passages and complex solos.
Influence of Musical Genres
The choice of pick and grip style varies significantly across different musical genres, affecting both sound and playability. For instance, the aggressive strumming in punk music may lead guitarists to favor thicker picks for a more pronounced sound, while the soft, subtle picking in fingerstyle guitar necessitates a lighter grip and thinner picks.
- Rock and Metal: Players in these genres often use thick picks to achieve a powerful sound, focusing on both strumming and precision picking. The grip is typically firm to control aggressive play.
- Jazz and Blues: Thinner picks are commonly favored, particularly for intricate picking patterns, with a looser grip allowing for fluidity and a more nuanced performance.
- Folk and Country: A balance between strumming and picking is often required, leading to a versatile grip that can adapt between techniques while maintaining control.
Famous Guitarists and Their Techniques
Examining the pick-holding techniques of renowned guitarists reveals the diversity in approaches influenced by individual styles and preferences. For example, Jimi Hendrix was known for holding his pick at an unconventional angle, allowing for a unique strumming technique that contributed to his signature sound. In contrast, classical guitarist Andrés Segovia often eschewed a pick, relying solely on fingerstyle techniques, showcasing how personal style can dictate even the choice of tools.
- Jimi Hendrix: Employed a loose grip with a unique angle, enhancing his dynamic strumming patterns.
- Eric Clapton: Combined fingerstyle and pick techniques, often using a medium pick held firmly for both strumming and melodic picking.
- Paco de Lucía: A master of flamenco guitar, he frequently used a combination of thumb and fingers, demonstrating a different approach altogether.
Exercises for Pick Control

Improving pick control is essential for any guitarist seeking to enhance their playing precision and speed. Effective exercises can help develop the necessary skills for better coordination and technique, which are critical for any musical style.Finger coordination is fundamental when using a guitar pick. It enables the musician to achieve a seamless connection between the pick and the strings, facilitating a more fluid playing style.
Developing finger coordination not only enhances pick accuracy but also aids in the overall control of the instrument. By honing these skills, players can navigate complex passages more effortlessly, resulting in a more polished sound.
Exercises to Improve Pick Accuracy and Speed
Incorporating specific exercises into your practice routine can greatly improve your pick control. The following exercises are designed to target various aspects of pick accuracy, speed, and coordination:
- Single String Picking: Focus on playing a single note repeatedly on one string. Gradually increase the tempo while maintaining precision. Aim for a clear and consistent sound with each pick stroke.
- Chromatic Scale Exercise: Play the chromatic scale across all six strings. Start slowly and increase speed as you become more comfortable. This exercise enhances finger dexterity and pick control.
- Alternate Picking: Practice alternate picking by picking down on one note and up on another. This helps develop the ability to switch between strokes efficiently, which is crucial for fast passages.
- Strumming Patterns: Work on various strumming patterns using a metronome. Focus on evenness and rhythm while changing between different patterns to build coordination.
- String Skipping: Practice skipping strings while maintaining a consistent picking motion. This exercise helps improve accuracy and coordination between your right hand and left hand.
Importance of Finger Coordination
Finger coordination is vital when using a pick, as it affects the timing and rhythm of your playing. It allows for the synchronization of hand movements, enabling smoother transitions between notes and chords. Developing this coordination can lead to improved technique and a more expressive sound.To strengthen finger coordination, players can engage in finger independence exercises, such as playing arpeggios or fingerpicking patterns that require individual finger movements.
These exercises enhance muscle memory and build a connection between the fingers and the pick, making it easier to execute intricate passages.
Practicing with a Metronome
Practicing with a metronome is an invaluable tool for developing timing and precision while using a pick. It instills a sense of rhythm and encourages players to maintain a steady tempo. Here are some tips for effectively using a metronome during practice:
- Start at a Slow Tempo: Begin with a manageable speed that allows for precise execution of notes before gradually increasing the tempo.
- Set Clear Goals: Focus on specific sections of a piece, practicing them with the metronome until you can play them confidently at a given speed.
- Vary the Tempo: Experiment with different tempos to challenge yourself and develop adaptability in your playing.
- Use Subdivisions: Incorporate subdivisions (such as eighth notes or triplets) to enhance your rhythmic accuracy while using the pick.
- Record Your Practice: Recording sessions can provide insights into your timing and accuracy, helping you identify areas for improvement.
“Practicing with a metronome not only improves timing but also builds confidence in your ability to maintain a steady rhythm while using a pick.”
Maintenance and Care for Your Picks
Taking proper care of your guitar picks is essential for prolonging their lifespan and ensuring optimal performance while playing. Regular maintenance can prevent wear and tear, keeping your picks in excellent condition for as long as possible. Understanding the different materials used in picks and how to care for each type is crucial for every guitarist.
Cleaning Methods for Different Types of Picks
Routine cleaning of guitar picks is vital to maintain their grip and performance. The cleaning method can vary depending on the material of the pick. Here are some effective techniques:
- Plastic Picks: Plastic picks can be cleaned simply by rinsing them under warm water and drying them with a soft cloth. For stubborn grime, a mild soap solution can be used.
- Celluloid Picks: These should be treated with care. Wipe them with a damp microfiber cloth to avoid scratches, and do not soak them in water as it can warp them.
- Wooden Picks: To clean wooden picks, use a dry cloth to remove dirt and oils. If necessary, a small amount of natural oil can be applied to maintain the finish, but excessive moisture should be avoided.
- Metal Picks: Metal picks can be polished with a metal polish cloth. Avoid using abrasive cleaners to prevent scratches, and store them in a way that minimizes exposure to moisture to prevent rusting.
Storage Solutions to Prevent Wear and Tear
Proper storage of your guitar picks is essential for preventing damage and loss. Consider the following methods to keep your picks safe and in good condition:
- Pocket Organizers: Use small pouches or organizers that can be kept in your guitar case or gig bag. This prevents picks from getting lost or damaged while transporting your gear.
- Pick Holders: A pick holder can be attached to your guitar or case, allowing easy access while keeping them secure from falling or getting scratched.
- Climate Control: Store your picks in a cool, dry place to avoid exposure to humidity which can warp or degrade certain materials.
- Inventory Management: Keep an inventory of your picks, noting the types and quantities. This can help in quickly assessing your collection and replacing picks when necessary.
Choosing the Right Pick Based on Playing Habits
Selecting the proper guitar pick is not just about personal preference but also about how it complements your playing style. Consider the following factors when choosing your pick:
- Thickness: Thicker picks provide more control and are often preferred for strumming, while thinner picks allow for greater flexibility, which can enhance techniques like fingerpicking.
- Material: Different materials affect the sound and feel. Nylon picks are known for their grip and flexibility, while acrylic options offer a brighter tone.
- Shape: While standard shapes are common, experimenting with different shapes can help you find one that fits comfortably and allows for ease of play.
- Surface Texture: Textured picks can provide a better grip, which is particularly helpful during intense playing sessions, reducing the risk of slips.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

As with any skill, beginners often encounter various challenges when learning to play the guitar with a pick. Addressing these issues not only enhances the playing experience but also contributes to overall skill development. Below, we explore some common problems faced by novice players, along with effective solutions to alleviate discomfort and improve technique.
Identifying and Solving Common Problems
Beginners may face several hurdles when first using a guitar pick. Recognizing these issues is the first step toward overcoming them. Here are some common challenges along with their corresponding solutions:
- Inconsistent Strumming: Beginners often struggle with maintaining a steady rhythm when strumming. A solution is to practice with a metronome to develop timing and consistency. Start slow, gradually increasing the speed as confidence builds.
- Dropping the Pick: Many new players experience dropping the pick during play. To combat this, ensure that the grip on the pick is firm but not overly tense. Utilizing picks with a textured surface can also improve grip.
- Unwanted Noise: Unwanted string noise often occurs when transitioning between picking and strumming. To address this, players can practice muting techniques with the palm of their picking hand, which can help control sound and improve clarity.
Overcoming Discomfort or Pain
Experiencing discomfort or pain while holding a pick can hinder progress and enthusiasm. Here are some tips to help alleviate these issues:
- Choose the Right Thickness: Picking discomfort can be influenced by the thickness of the pick. Beginners should experiment with varying pick thicknesses to find one that feels comfortable and provides adequate control.
- Adjust Grip Technique: A common source of pain is an improper grip. The pick should be held between the thumb and first finger, with only a small portion of the pick protruding. This allows for greater control and reduces strain.
- Take Breaks: Prolonged playing can lead to muscle fatigue. Regular breaks during practice sessions can help reduce discomfort and prevent potential injuries.
Smooth Transitioning from Fingerstyle to Pick Playing
Transitioning from fingerstyle to playing with a pick can be a smooth process with the right approach. Here are some suggestions to facilitate this change:
- Practice Scales with a Pick: Begin by practicing scales using a pick to develop a feel for the instrument. Start with simple patterns to build confidence.
- Incorporate Simple Songs: Choose easy songs that predominantly use a pick. This makes the transition enjoyable while solidifying the new technique.
- Focus on Picking Techniques: Work on basic picking techniques, such as alternate picking and downstrokes. Gradually increase complexity as comfort with the pick improves.
“Mastering the pick technique is essential for developing a unique playing style that enhances musical expression.”
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the art of holding a guitar pick correctly is a vital skill that can greatly influence a guitarist’s performance and enjoyment of music. By applying the techniques discussed, including the proper grip and care for your picks, players can overcome common challenges and cultivate their unique sound. Whether strumming chords or executing intricate solos, mastering this skill will undoubtedly lead to a more fulfilling musical journey.