How to Adjust Your Amp for a Live Gig is a crucial skill for musicians aiming to deliver their best performance on stage. Mastering your amplifier settings can significantly enhance your sound quality and ensure that your music resonates well with the audience. This guide delves into the intricacies of amplifier controls, the importance of venue acoustics, and offers practical tips on achieving that perfect tone for any genre.
From understanding the basic functions of amplifier controls to troubleshooting common issues during performances, this comprehensive overview equips you with the tools necessary to navigate the complexities of sound adjustments. By the end of this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to adapt your amp settings for various venues, ensuring an exceptional live performance each time.
Understanding Amplifier Settings
Amplifier settings play a crucial role in shaping the sound of an instrument, especially during live performances. The right adjustments not only enhance the tonal quality but also ensure that the audio output is balanced and appropriate for the venue. In live gigs, where acoustics can vary significantly from one location to another, mastering amplifier settings is essential for achieving the desired sound.Amplifiers typically feature a range of controls that allow musicians to modify their sound output.
Understanding these controls is vital for optimal performance. The most common controls found on amplifiers include:
Common Amplifier Controls and Their Functions
The following details the typical controls found on amplifiers and their respective functions. Familiarity with these settings can significantly impact sound quality during a live gig.
- Gain: This control adjusts the input signal strength. Higher gain settings can produce more distortion, which may be desirable for certain genres like rock.
- Treble: This control adjusts the high frequencies of the sound. Increasing the treble can add clarity and brightness to the tone.
- Midrange: This control affects frequencies in the middle range. It is crucial for shaping the body of the sound and can help instruments stand out in a mix.
- Bass: This setting controls the low frequencies. A boost in bass can add depth and warmth to the music, which is particularly beneficial for genres like jazz and blues.
- Reverb: This effect adds a sense of space and depth to the sound. Adjusting reverb levels can create a more ambient or intimate feel, depending on the performance context.
Different music genres often require distinct amplifier settings to achieve the desired sound. The following examples illustrate typical amplifier settings tailored for various styles of music:
Typical Amp Settings for Different Music Genres
When preparing for a live performance, adjusting your amplifier settings according to the genre can greatly enhance your sound. Here are some common settings based on genre:
- Rock: Gain at a higher level (7-9), treble boosted (6-8), midrange moderate (4-6), and bass moderately high (5-7) can create a full, aggressive tone.
- Jazz: Lower gain settings (3-5), moderate treble (4-6), enhanced midrange (6-8), and slightly boosted bass (5-6) provide a warm, smooth sound.
- Metal: High gain (8-10), treble and midrange (7-9), with bass at moderate levels (5-7) delivers a heavy, powerful sound suitable for aggressive styles.
- Blues: Moderate gain (5-7), treble (5-6), midrange (6-8), and bass (5-7) settings help achieve a rich, expressive tone characteristic of blues music.
- Pop: Balanced settings with gain (5-6), treble (5-7), midrange (5-6), and bass (5-6) create a versatile sound adaptable across various pop styles.
Understanding and effectively utilizing amplifier settings is essential for musicians performing live. Each control contributes to the overall sound, allowing for tailored adjustments to suit different musical contexts and personal preferences.
Preparing for the Venue

When preparing to adjust your amplifier for a live performance, it is crucial to consider the specific characteristics of the venue. Each location has unique acoustics, dimensions, and sound qualities that can significantly influence the overall sound of your performance. Understanding these factors will help you optimize your amplifier settings to ensure the best sound for your audience.One of the primary factors influencing sound adjustment is the acoustics of the room.
Different materials and structures within a venue can affect how sound travels and resonates. For instance, a venue with hard surfaces, such as wood or concrete, may create a brighter and more reflective sound, while a space with soft furnishings may absorb sound and create a warmer tone. Recognizing these differences can guide you in setting your amp to complement the room’s characteristics.
Role of Room Acoustics in Sound Adjustment
Room acoustics play a pivotal role in sound quality and clarity during a live performance. The following considerations can help you understand how to adjust your amplifier effectively:
- Size of the Venue: Larger venues often require more power and may necessitate adjustments to both volume and tone settings to fill the space adequately.
- Ceiling Height: High ceilings can lead to echo and reverberation; in such cases, reducing bass frequencies may help maintain clarity.
- Surface Materials: The materials that make up the walls, floor, and ceiling can drastically influence sound reflections. For example, a venue with many glass surfaces may create bright and sharp reflections, while a venue with heavy curtains may soften the sound.
- Audience Size and Placement: The number of people in the audience and their placement can affect how sound travels. A packed venue will absorb sound differently than an empty one, which may require further adjustments to your amp’s settings.
Understanding these acoustic variables can lead to a more focused and refined sound, allowing your performance to resonate well with your audience.
Checklist for Setting Up Your Amp Before a Performance
Having a well-defined checklist can ensure that you don’t overlook critical aspects when setting up your amplifier for a live show. Here are key items to consider:
- Inspect Your Equipment: Ensure your amplifier, cables, and any pedals are in working order to avoid technical difficulties.
- Test the Sound: Play a few notes to gauge the sound in the venue. Adjust your settings according to the initial feedback from the acoustics.
- Adjust Volume Levels: Start with lower volume settings to avoid feedback and gradually increase to a comfortable level.
- EQ Settings: Based on the venue’s acoustics, tweak your equalization settings to enhance clarity and reduce muddiness.
- Monitor Placement: Position your monitors appropriately to ensure you can hear yourself clearly without excessive volume.
- Backup Plan: Always have a backup plan in place for equipment failure, including spare cables and a backup amp if possible.
Following this checklist can help streamline your preparation process and lead to a more successful live performance.
Dialing in Your Sound
Setting the right sound during a live performance is crucial for delivering an engaging experience to your audience. This process, known as dialing in your sound, involves carefully adjusting your amplifier settings to achieve a balanced tone that complements your musical style and the venue’s acoustics. During the soundcheck, you will have the opportunity to refine these settings, ensuring that your performance is both powerful and sonorous.During the soundcheck, start by playing a few chords or melodies that you typically use in your set.
This helps you and the sound engineer assess the overall sound in relation to the venue’s acoustics. Focus on adjusting the EQ settings—typically bass, midrange, and treble—to find a harmonious balance. It may be beneficial to keep in mind the characteristics of the venue; for example, a smaller space may amplify low frequencies, necessitating a reduction in bass settings.
Achieving a Balanced Tone
A balanced tone can significantly enhance your live performance. Here are some techniques to help you achieve this:First, consider the role of each frequency band:
- Bass: Provides depth and warmth, but too much can muddy the sound. Aim for clarity by reducing bass when necessary, especially in smaller venues.
- Midrange: Essential for presence; be mindful of cutting too much, as it can lead to a thin sound. Adjust midrange frequencies to ensure your instrument cuts through the mix.
- Treble: Adds brightness and definition. However, excessive treble can cause harshness, so make subtle adjustments to maintain smoothness.
It is also essential to consider the context of your performance. The balance of your sound may need to change depending on whether you are playing solo, in a band, or with backing tracks. Always trust your ears and seek feedback from your bandmates or sound engineer to ensure a well-rounded mix.
Impact of Gain Levels
The gain settings on your amplifier play a critical role in shaping your overall sound. Different gain levels can dramatically impact the character of your tone:
- Low Gain: Produces a clean sound with minimal distortion, ideal for genres like jazz or pop where clarity is key.
- Medium Gain: Introduces a slight overdrive, offering warmth and sustain without overwhelming distortion, suitable for rock or blues.
- High Gain: Delivers a saturated tone, perfect for heavier genres like metal or hard rock. However, be cautious, as excessive gain can lead to a loss of definition in your playing.
Adjusting your gain levels should be done in conjunction with other settings to ensure you maintain clarity and tone. A well-rounded approach to gain, along with your EQ settings, will help you achieve the desired sound for your live performance.
Finding the right gain balance is essential for achieving a tone that resonates with your audience while allowing your instrument to shine through.
Utilizing Effects and Pedals

Integrating effects pedals with your amplifier settings can significantly enhance your performance, providing a more dynamic and textured sound. Understanding how to properly adjust your amp in conjunction with these effects is essential for achieving the desired tone and impact during a live gig.Effects pedals can dramatically alter the characteristics of your sound, influencing everything from your basic tone to your dynamic expression.
They can add depth, color, and nuance, making it vital to understand how these effects interact with your amplifier settings. Properly setting your amp while taking into account the effects you are using ensures a cohesive sound.
Integration of Effects Pedals with Amp Settings
When integrating effects pedals with your amplifier, consider the following guidelines for optimal results:
1. Order of Effects
The sequence in which you connect your effects pedals can drastically change your sound. Typically, distortion and overdrive pedals are placed before modulation effects like chorus or flanger. This order allows for a warmer, richer tone.
2. Gain Structure
Adjust your amp’s gain to accommodate the added signal from your effects pedals. Too much gain can lead to unwanted distortion, while too little can make your sound thin. For example, if using a delay pedal, ensure that the gain is set to avoid muddiness.
3. Effects Loop
Utilize the effects loop of your amplifier for time-based effects such as reverb and delay. This placement ensures that these effects maintain clarity and depth, as they are processed after the preamp stage.
4. Mix Levels
Adjust the mix levels on your pedals to find a balance between the dry (unaffected) sound and the wet (effected) sound. This allows your natural tone to shine through while enhancing it with effects.
Impact of Different Effects on Live Sound
Different effects have unique impacts on live sound, necessitating careful amp adjustments to complement each effect. Here are some popular effects and their influences:
Overdrive/Distortion
Increases harmonic content and sustain, often requiring a reduction in gain to avoid overly aggressive tones.
Chorus
Adds a shimmering quality to the sound, benefiting from slight adjustments to mid-range frequencies to maintain clarity.
Reverb
Creates a sense of space. Adjust the amp’s EQ to compensate for any muddiness introduced by reverb; typically, cutting the low frequencies can help maintain clarity.
Delay
Can thicken the sound without being overly pronounced. Adjusting the feedback settings and mix level helps ensure the delay complements rather than overwhelms the original tone.
Guidelines for Choosing Effects Based on Genre
Selecting the right effects for your musical style is crucial for achieving the appropriate sound. Below are guidelines based on different music genres:
Rock
Overdrive and distortion pedals are essential, along with delay and reverb for solos. A classic setup may include a fuzz pedal for a heavier sound.
Blues
A smooth overdrive pedal paired with a compressor can enhance sustain while maintaining dynamic range. Adding a light chorus can add depth.
Metal
High-gain distortion pedals are a must, often complemented by noise gates to control feedback. Reverb should be kept minimal to maintain clarity in complex riffs.
Jazz
A clean boost can enhance dynamics without altering tonal characteristics. Delay and reverb are often used subtly to create depth without overshadowing the natural tone.
Pop
A versatile setup with modulation effects such as chorus and flanger, along with delay and reverb, can provide lush soundscapes, requiring careful balancing with the amp’s EQ.Utilizing effects and pedals effectively requires an understanding of how they interact with your amplifier settings. By carefully considering the order of effects, gain structure, and adjustments based on genre, musicians can achieve a polished and professional sound that resonates powerfully with their audience.
Monitoring and Feedback Control
Monitoring and feedback control are crucial elements of a successful live performance. Properly setting up a monitoring system ensures that musicians can hear themselves clearly, which is essential for maintaining pitch and timing. Additionally, understanding feedback issues and implementing strategies to minimize them can significantly enhance audio quality and overall performance.
Setting Up Your Monitoring System
An effective monitoring system allows performers to hear their instruments and vocals accurately. This is particularly important in loud environments where stage noise can mask sounds. To set up your monitoring system, consider the following steps:
1. Choose the Right Monitors
Select stage monitors that best suit the venue size and your audio needs. Floor wedges are commonly used, but in-ear monitors provide a more controlled sound and can help reduce feedback risks.
2. Positioning
Place the monitors at an appropriate distance and angle from the performers. Ideally, they should be directed towards the musician’s ears to enhance clarity while minimizing stage bleed.
3. Sound Check
Conduct a thorough sound check before the performance. Adjust the monitor levels so that each musician can hear themselves and each other clearly without excessively high volumes that could lead to feedback.
4. Personal Volume Control
Utilize personal mixers, if available, allowing performers to adjust their monitor mix to their preference, which can enhance performance comfort and effectiveness.
Common Feedback Issues and Resolutions
Feedback occurs when the sound from the speakers is picked up by the microphones, creating a loop that results in a high-pitched noise. Understanding common feedback issues can help in troubleshooting effectively.
1. Microphone Placement
Feedback often arises from improper microphone placement. Ensure that microphones are positioned close to the source but away from direct speaker output.
2. Equalization (EQ) Adjustments
Use EQ settings to cut frequencies that are prone to feedback. These typically include mid-range frequencies. A graphic or parametric equalizer can help identify and reduce specific problematic frequencies.
3. Volume Levels
Excessively high overall volume levels on stage can lead to feedback. Lowering the gain on microphones or reducing the overall stage volume can mitigate these issues.
4. Room Acoustics
Understand the venue’s acoustics as reflections from walls can exacerbate feedback. Using acoustic treatment or strategically placing sound-absorbing materials can help control reflections.
“Preventing feedback is as much about understanding your environment and equipment as it is about managing volume levels.”
Tips for Adjusting Amp Settings to Minimize Feedback
Adjusting amplifier settings is pivotal in preventing feedback during live performances. Here are some useful tips:
Gain Structure
Set the gain levels on your amplifier to a point where the sound is clear but not distorted. A lower gain can help prevent feedback.
Use of High-Pass Filters
Engage high-pass filters on your mixer or amplifier channels. This can effectively reduce low-frequency rumble that can contribute to feedback.
Dynamics Processing
Implement compressors to manage peak levels that may cause feedback. This allows for a smoother sound without sudden spikes that can lead to ringing.
Stage Layout
Adjust the physical setup of the stage to ensure sufficient distance between microphones and speakers. Creating space can significantly reduce the potential for feedback loops.By implementing these strategies, performers can optimize their monitoring systems, address feedback issues, and adjust their amplifier settings to create a more enjoyable and professionally sounding live performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

During live performances, amplifiers can encounter various issues that may disrupt sound quality and affect the overall experience for both the musician and the audience. Understanding these common problems and knowing how to address them can ensure a smoother performance. This section provides insights into typical amplifier-related problems and effective troubleshooting techniques.
Common Amplifier Problems and Solutions
It is essential to recognize and address common amplifier issues that may arise during a gig. The following list Artikels several frequent problems, their potential causes, and effective solutions.
- Distorted Sound:
Distortion can occur if the amplifier is set too high or if there is a fault in the signal chain.
- Check and lower the gain settings.
- Ensure all cables are properly connected and not damaged.
- Use the amplifier’s tone controls to adjust EQ settings.
- Loss of Power:
A sudden drop in volume often indicates a power issue or a problem with the speaker.
- Inspect power cables and connections for any faults.
- Test with a different power outlet or use a power conditioner.
- Check speaker connections and replace any blown fuses.
- Feedback Loops:
Feedback can create unwanted noise and is often caused by microphone placement.
- Adjust microphone positioning to minimize pickup from the speakers.
- Lower the volume of the channels that are feeding back.
- Utilize a feedback eliminator or notch filter for quick adjustments.
Troubleshooting Flowchart for Sound Issues
A systematic approach to troubleshooting can greatly assist in identifying the root cause of sound problems during a performance. Below is a flowchart that Artikels the steps to take when encountering sound issues on stage:
1. Identify the Problem
Is the sound distorted, too quiet, or causing feedback?
2. Check Connections
Ensure all cables are securely connected and undamaged.
3. Adjust Settings
Modify gain, volume, and EQ settings to see if the issue resolves.
4. Isolate Components
Test individual components like the amp, guitar, and pedals to identify the source of the problem.
5. Seek External Help
If none of the above solutions work, consult a technician or sound engineer for assistance.
Examples of Quick Fixes for Real-Time Adjustments
In the fast-paced environment of a live gig, quick fixes can save a performance from becoming compromised. The following examples illustrate methods to swiftly adjust sound on stage:
- Using a Compressor:
A compressor can help level out volume inconsistencies. Quickly engage it to smoothen out sudden spikes. - Adjusting the Reverb:
If the sound is too dry, a quick twist of the reverb knob can add depth without a lengthy setup. - Channel Switching:
If one channel is producing issues, switching to a backup channel can provide an immediate alternative.
Post-Gig Review
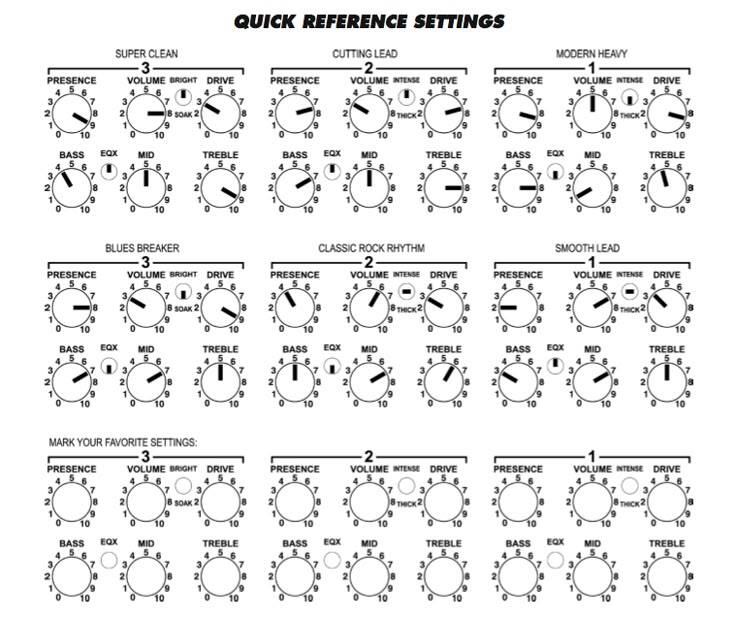
After a live performance, the post-gig review is a critical step that often goes overlooked by musicians. This process not only allows for reflection on the performance but also serves as an opportunity to assess and adjust amplifier settings based on real-world experience. By evaluating the sound quality during the gig, musicians can make informed decisions that enhance future performances.Documenting amp settings after each gig is crucial for continual improvement.
By keeping a record, musicians can replicate successful configurations and avoid previous pitfalls. This practice leads to a more consistent sound and a deeper understanding of how various settings impact performance in different environments.
Framework for Evaluating Sound Quality
To effectively evaluate sound quality after a gig, musicians can follow a structured approach. This framework aids in identifying areas for improvement and refining amplifier settings for future shows. The following points can serve as a guide:
1. Sound Clarity and Definition
Analyze whether each instrument was clearly audible and well-defined. Pay attention to frequencies that may have been muddled or harsh.
2. Balance among Instruments
Assess how well the sound mixed with other instruments. A balanced mix ensures that no single element overwhelms the others, contributing to a cohesive performance.
3. Volume Levels
Evaluate the overall volume levels. Consider whether the sound was too loud, leading to distortion, or too soft, causing it to be lost in the venue’s acoustics.
4. Audience Feedback
Gather feedback from audience members regarding the sound quality. Their perspective can offer valuable insights that musicians may not notice while performing.
5. Personal Experience
Reflect on personal comfort while performing. Consider if the sound was engaging, or if there were moments when adjustments were necessary to enhance the performance experience.
6. Setting Documentation
Create a detailed record of the amp settings used, including EQ adjustments, gain levels, and effects. This documentation will assist in recreating a favorable sound in similar venues.
7. Identify Issues
Take note of any technical problems experienced during the gig. Documenting these issues can help in troubleshooting and making necessary adjustments for future performances.
“Reflecting on the sound quality not only prepares you for your next performance but also enhances your growth as a musician.”
Utilizing this framework can lead to significant improvements in sound quality, ensuring that each performance is better than the last. With diligent documentation and reflection, musicians can harness their experiences to refine their craft and deliver memorable performances.
Epilogue

In summary, effectively adjusting your amp for a live gig is not just about the technical settings; it’s about enhancing the overall musical experience for both you and your audience. By taking the time to review and document your amplifier settings after each performance, you can continuously improve and refine your sound. Embrace these insights, and let them guide you toward becoming a more confident and skillful performer.